
This is the first in a series of articles developed from Dr. Chris Hardy’s live presentation at Dragon Door’s Inaugural Health and Strength Conference.
I was 23 years old and had graduated from one of the toughest schools in the military. It was designed to mentally and physically beat you down. After 5-6 months, I came out thinking I was super human—of course at 23 we think that anyway. We were crushed with physical training twice a day with academics in between. But, when I graduated, I really didn’t know anything about training others. I thought training and getting better was all about getting beat down as hard as possible. But, I didn’t know that I would soon be facing a different challenge.
When I arrived at my new unit as the new guy, and they put me in charge of their training. They were all seasoned deep sea divers—a very physically demanding job, probably one of the hardest on the planet. Training military divers is like training athletes. They’re a very resilient, self-selected group. My dive school class started with 35, and 13 graduated. So the people who graduate are pretty hard to break. They put me in charge of their training, and over the next two years I developed my own routine of mashing them as hard as I could, because that’s what they wanted.
 During that same time, I got interested in medicine. I didn’t always want to be a doctor, but at 25, I decided I needed a change of pace. I went to college and thought that since I was already a trainer, I would train people while I went to college.
During that same time, I got interested in medicine. I didn’t always want to be a doctor, but at 25, I decided I needed a change of pace. I went to college and thought that since I was already a trainer, I would train people while I went to college.
I was used to dealing with military deep sea divers, and all I was working with people who have diseases and were out of shape. I didn’t know how to deal with any of these conditions and it blew my mind. I decided to learn more and started getting certifications. Over the next 20 years, I tried to hone my training craft and I even became a doctor along the way!
I wanted to know how to get results for these people without breaking them in the process. I couldn’t train them like Navy divers, because they wouldn’t come back and I would certainly break them. In 22 years as a trainer, and 12 years as a physician I don’t have all the answers, but I have developed a framework.
Your clients want results from you, but what’s your responsibility to them? Safety, or as in medical terminology, “do no harm”. We want them to achieve their goals, but we want them to do it safely. Sometimes you have to save your clients from themselves, because they think they know what they want but you really need to educate them. We also have a popular culture that creates more challenges for us in the perception of what exercise and weight loss should be like.
 TV shows like The Biggest Loser and other transformation programs are what our clients are seeing. They’re getting the message that every workout needs to be a beat-down, and if you’ve watched that show or others like it, there’s a calorically restricted diet. And that’s what our clients think will get them results. How many of you have new clients come to you expecting that kind of workout—and who aren’t happy when they don’t get it? Or maybe you aren’t getting clients because they are too scared to even come to your gym.
TV shows like The Biggest Loser and other transformation programs are what our clients are seeing. They’re getting the message that every workout needs to be a beat-down, and if you’ve watched that show or others like it, there’s a calorically restricted diet. And that’s what our clients think will get them results. How many of you have new clients come to you expecting that kind of workout—and who aren’t happy when they don’t get it? Or maybe you aren’t getting clients because they are too scared to even come to your gym.
We have a huge opportunity. As a good coach, we need to educate our clients on why the beat down workouts are not a good approach.
What is Coaching?
Coaching is an art with a scientific foundation. If you’re a professional, you have the art down, so now we will look at our foundation to answer some key questions:
- How can I optimally dose the training on any given day for my client?
- How can I prevent overdosing but still training the client hard enough so that they achieve their goals?
We aren’t letting our clients off the hook, this is the holy grail of training.
When I look at any problem, I want to go back to underlying foundations—that’s how I wrote Strong Medicine, and it’s how I approach medicine. I look at the foundations of the problem in the first place—it’s what I call first principles. Next, we can build a conceptual framework to answer the questions from the bottom up.
Before we could build a space shuttle, we first had to figure out how to make fire. In building up our conceptual framework, let’s begin by defining exercise. Exercise is a form of stress. What is stress? , Hans Selye defined stress as an engineering term as the amount of force per unit area. Now we say, “I’m under a lot of stress” or, “I am stressed out”.

Anything that triggers the stress response is a stressor—including exercise. Getting attacked by a bear, traffic, or doing dumbbell presses are all sources of stress. External stress examples include food, water, activity, your work environment, traffic. Internal stress can come from diseases—it all activates in the brain.
Is Stress Good or Bad?
Both, it depends. Short term stress is necessary for survival and if you want to make any gains in the gym. Marty Gallagher will tell you that, you can’t have sub-optimal stress if you want to make gains in the gym. But the chronic stress in an over-trained endurance runner or someone who is just completely burned out at their job is not good.
These chronic stresses actually lead to physical changes in the brain and nervous system, and over-activates our stress response. You could argue that the modern environment has toxic levels of stress and that our physiology is at odds with our modern environment. We are probably not wired to handle what we’re dealing with on a daily basis. We can easily recover from short term acute stress, and most of the time we’re not under it. But, many people are now under constant chronic stress, including your clients. And, you can’t train your clients as if they live in a vacuum.
 The brain is command central for the stress response. It receives, evaluates, and responds to stress in our environment from all sources. It is very important to understand that stress is everything the brain perceives as stress—whether or not the issue is a threat to life or limb. If your brain perceives something as stress, then you will trigger the stress response.
The brain is command central for the stress response. It receives, evaluates, and responds to stress in our environment from all sources. It is very important to understand that stress is everything the brain perceives as stress—whether or not the issue is a threat to life or limb. If your brain perceives something as stress, then you will trigger the stress response.
It is especially true in modern society. If your boss is a real jerk and you’re under stress at work, that same fight or flight response will be active as if you were running from a bear—maybe not to the same degree, but it will still be active.
We have fast and slow pathways. Simply put, the hypothalamus is a very small part of the brain but it’s actually central to the stress response. When the brain perceives something threatening—if someone scares you—then you get that fluttering heart, “all-jacked-up” feeling. That’s the fast pathway, and it’s direct to the adrenal glands. It dumps adrenaline, epinephrine, and norepinephrine. Afterwards, about twenty minutes later, the slow pathway through the pituitary gland and down to the adrenals is active. It’s a hormonal system that secretes cortisol which helps you recover from the stress. For the purposes of this post, that’s all you need to know about neuro-anatomy.
Those of you who have also trained in Chinese Medicine or follow Taoist philosophy know that the Yin/Yang concept works very well to describe the autonomic nervous system. (Autonomic just means that I don’t have to think about it for it to happen—I don’t have to think to raise my heart rate or to breathe at night.) The autonomic nervous system has two branches, sympathetic (fight or flight), and parasympathetic (rest and recovery). The “fight or flight” system is actually the most inflammatory response in the body. The parasympathetic system is the opposite. Typically, the parasympathetic system should be dominant most of the time, and the sympathetic should only be active when we need to use it for a “flight or fight” response or during exercise. The sympathetic system is used in response to stress—but it should be used minimally.
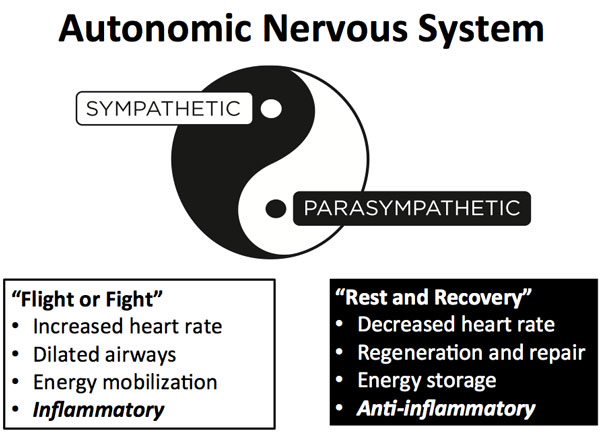
The parasympathetic system is dominant for the recovery to all of the exercise you’re doing (and that your clients are doing). It’s also when that anabolic response to exercise occurs. But, if the sympathetic system is on all the time—as it is for many of our clients and ourselves—in the long term it will lead to muscle-wasting and chronic diseases.
How the Brain Controls Stress Response
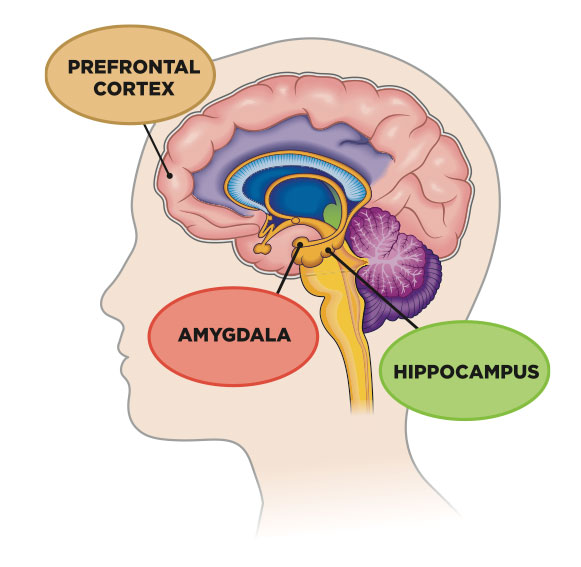
Three main parts of the brain control the stress response to perceived threats. The prefrontal cortex (we also use it to maintain attention) right behind the forehead determines if something is truly a threat using higher reasoning. Our memory center, the hippocampus also helps us determine if something is threatening or not. The prefrontal cortex and hippocampus can override the threat response together if they have determined something has been seen or experienced before and is probably not threatening. The amygdala is the brain structure which drives the threat response, it responds to learned fear and the emotional reaction of stress. If I got an electric shock every time someone rang a bell or hit a gong, then pretty soon every time I would hear a sound like that, I would have a severe stress response. That’s what the amygdala does.
Normally, the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex inhibit the stress response, and the amygdala will activate it. It’s a three prong connection, and the brain will perform normally if the parasympathetic system is dominant most of the time. For example, if you see long cylindrical object across your path while walking in the woods, the prefrontal cortex will pay attention to it, the hippocampus will respond that it recognizes that it’s probably a stick, and will generally keep the brain from triggering the stress response.
 But over time, a brain will change in response to chronic stress. The word neuroplasticity means that the brain can functionally and structurally change. We used to think that psychological stress was “all in your head”, but in fact the brain can change its structure and how it functions—and you can actually be lose neurons. A person who is stressed out or depressed over a long term will have a physically different brain—the hippocampus will shrink under chronic stress.
But over time, a brain will change in response to chronic stress. The word neuroplasticity means that the brain can functionally and structurally change. We used to think that psychological stress was “all in your head”, but in fact the brain can change its structure and how it functions—and you can actually be lose neurons. A person who is stressed out or depressed over a long term will have a physically different brain—the hippocampus will shrink under chronic stress.
Epigenetics is how the genes in our DNA are expressed. In Strong Medicine, I used this example: genes are a recipe that says I need four eggs to make a cake. So, if I do a mutation and use five eggs, then that’s a mutation to the genes. Epigenetics doesn’t change the genes, it just tells me how many “cakes” (if any) will be made from the recipe. When someone is under constant stress, everything is involved including hormone pathways. Everything involved with the stress response will be amped up and producing more products for the stress response.
So, someone under chronic stress will respond differently to exercise. If their stress response is overactive, it won’t take much to activate it, and they will have a harder time recovering from exercise because the sympathetic nervous system will be more dominant. If they are already in such a fight or flight state, it will take longer for the parasympathetic nervous system to allow for recovery. Normally the brain would use these mechanisms for survival, not a chronic perceived stress.

Going back to our example with the stick across a path in the woods, if the brain is under chronic stress it will become more animal-like. The structure has changed and when someone with a chronically stressed brain sees something lying across the path, and the hippocampus memory has shrunk, you might jump straight to the conclusion that the object is a snake and trigger the stress response. The chronically stressed brain responds and reacts as opposed to focusing, maintaining attention, and drawing on previous memories.
How does all of this relate to fitness and training? As trainers—and I’ve done this myself—we often focus only on physical stresses. But, we aren’t training in a vacuum, so we must consider our environments. Our clients are faced with many sources of stress outside exercise stress, and we want to train them effectively. Allostasis is a broad concept that basically means “achieving stability through change”. While homeostasis means that a specific equilibrium is maintained, allostasis changes the point we come back to maintain that equilibrium. The stress response is part of this process. If you are trying to achieve stability with the environment, then we are also trying to achieve stability with anything perceived as threatening, challenging, or dangerous, right?
Allostasis is the mechanism responsible for adaptation to any challenge, exercise, or social, psychological activity. We need some psychological stress to become resilient, but too much of it and we can become depressed and anxious. Nutrition is similar, we need to be adequately nourished but not overly so, since the body will adapt to over-nutrition, and we see that all the time. The same is also true for sleep—too little sleep and the body adapts with a stress response, and new science is showing that too much sleep is also bad.
As far as the brain is concerned, recovering from a training challenge with endorphins, and growth hormone building bigger muscles and more mitochondria is allostasis—the brain will think that you need to get stronger to survive that type of challenge/stress again. Allostasis brings you to a new set point as opposed to homeostasis taking you back to the same equilibrium. This is a relatively new concept. Total stress is also called the allostatic load—allostasis is the change, and allostatic load is everything that the brain perceives from the environment as stress.
***
The next post in this series will outline a visual representation of the Stress Cup and how to use it to optimize your training and client training programs.
Chris Hardy, D.O., M.P.H., CSCS, is the author of Strong Medicine: How to Conquer Chronic Disease and Achieve Your Full Genetic Potential. He is a public-health physician, personal trainer, mountain biker, rock climber and guitarist. His passion is communicating science-based lifestyle information and recommendations in an easy-to-understand manner to empower the public in the fight against preventable chronic disease.